New Paragraph
Is Gum Disease Infectious? Debunking Myths and Sharing Prevention Tips
Have you ever thought about whether gum disease is contagious? It’s a question many people have, especially when sharing food or drinks. While gum disease itself isn’t contagious like the flu, the bacteria responsible for it can spread from person to person through saliva.
In this article, we'll break down how gum disease works, how it can be transmitted, and what you can do to protect yourself and those around you. Let’s get into the facts and keep your gums healthy!
Understanding Gum Disease
The health of your gums plays a vital role in your overall well-being. Gum disease, if left unchecked, can have serious consequences for your oral and overall health. To grasp the contagious nature of gum disease, it's essential to understand the condition itself.
Essentially, gum disease is an inflammatory response triggered by the buildup of plaque on teeth and along the gum line. Plaque is a sticky film teeming with bacteria that constantly forms on your teeth. When plaque isn't adequately removed through regular brushing and flossing, it hardens into a rough deposit called tartar, which can irritate your gums and lead to inflammation.
What is Periodontal Disease?
Periodontal disease, frequently referred to as gum disease, signifies an infection that impacts the tissues responsible for supporting and surrounding your teeth. These tissues comprise the gums, periodontal ligaments, and alveolar bone. This prevalent oral health condition arises from a bacterial infection that causes inflammation, and if left untreated, it can destroy the gum tissue and bone that support your teeth, potentially leading to tooth loss.
Periodontal disease often begins with gingivitis, an early and milder form characterized by inflamed gums that may bleed easily during brushing or flossing. Without intervention, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, marked by the formation of pockets between the gums and teeth.
These pockets create spaces where bacteria can accumulate, further inflaming the gums and eventually damaging the supporting structures of the teeth. Understanding the progression of periodontal disease is essential for appreciating the importance of early detection and treatment in maintaining optimal oral health.
The Causes and Risk Factors of Gum Disease
Primarily, gum disease stems from the buildup of plaque on teeth, which is directly linked to poor oral hygiene. When you don't brush and floss diligently, plaque accumulates, providing a breeding ground for bacteria. These bacteria release toxins that irritate and inflame the gums, marking the initial stage of gum disease.
Beyond inadequate oral hygiene, several factors can heighten your risk of developing gum disease. Tobacco use, in any form, is a significant risk factor. Smoking weakens your body's immune system, making it harder for your body to fight off infections, including those affecting your gums. Additionally, smoking impairs blood flow to the gums, hindering the delivery of essential nutrients and oxygen required for healing.
Furthermore, certain medical conditions like diabetes can make you more susceptible. Diabetes affects blood sugar control, which can impair the body's ability to heal and combat infections, increasing your vulnerability to gum disease.
Hormonal changes, particularly during pregnancy or menopause, can also elevate the risk due to hormonal fluctuations influencing gum sensitivity. Genetics also plays a role, as some individuals may be genetically predisposed to gum disease.
The Contagious Nature of Gum Disease
Now, let's address the question that brought you here: Is gum disease truly contagious? While you won't contract gum disease simply by being near someone who has it, the bacteria responsible for this prevalent oral health concern can be transmitted.
The transmission occurs primarily through the exchange of saliva, which can happen through activities like kissing, sharing eating utensils, or even using someone else's toothbrush. Therefore, while not considered airborne like a cold or the flu, certain behaviors can increase the likelihood of transferring the bacteria that contribute to gum disease.
How Gum Disease Spreads Between People
While we've established that gum disease itself isn't a contagious disease like the common cold, the bacteria that cause it can be transmitted from one person to another through saliva contact. This exchange of saliva can occur in several ways, and understanding these modes of transmission is key to minimizing your risk.
One of the most common ways gum disease-causing bacteria spread is through kissing. When you kiss someone, you inevitably exchange saliva, potentially transferring bacteria. Similarly, sharing eating utensils, drinking from the same glass, or using someone else's toothbrush can also facilitate the transmission of these bacteria.
It's important to note that while the exchange of saliva can introduce gum disease-causing bacteria into your mouth, it doesn't automatically mean you'll develop the condition. Several factors influence whether exposure leads to infection, including the health of your immune system and your oral hygiene practices.
Misconceptions About Gum Disease Transmission
A common misconception surrounding gum disease is that it can spread through casual contact, like shaking hands or breathing the same air. However, this isn't the case. Gum disease isn't an airborne illness, so it cannot be transmitted through the air like a cold or flu virus.
Another misconception is that sharing food or drinks necessarily leads to gum disease transmission. While sharing utensils or drinking from the same glass as someone with gum disease can increase the risk of spreading, simply sharing food or drinks without this direct contact is unlikely to transmit the bacteria.
The risk of spreading gum disease through casual contact is minimal. The bacteria responsible for gum disease are typically spread through direct contact with infected saliva.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Gum Disease
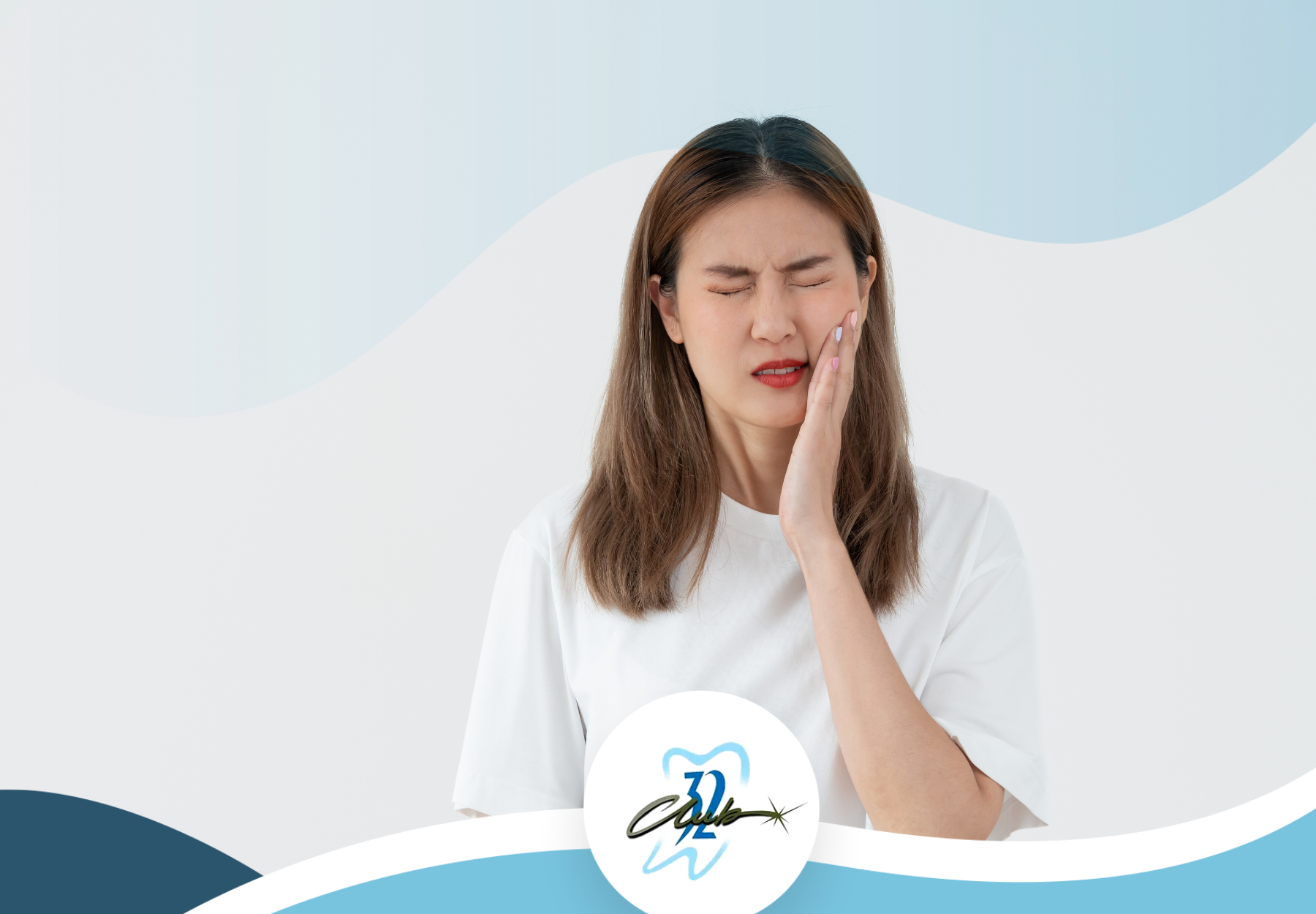
Early detection and treatment of gum disease are vital in preventing its progression and preserving your oral health. Therefore, recognizing the signs and symptoms is crucial. If you notice any of the following warning signs, it's essential to schedule an appointment with your dentist.
Red, swollen, or tender gums, bleeding while brushing or flossing, persistent bad breath, receding gums, loose or shifting teeth, or changes in your bite should all be causes for concern. These could indicate the presence of gum disease, and a professional evaluation is recommended.
Recognizing the Signs of Gum Disease
Being attentive to your oral health is essential for identifying potential problems early on. Gum disease, in its initial stages, may not present noticeable symptoms, but as it advances, several warning signs can alert you to its presence. Observing these warning signs and taking prompt action can help prevent further damage and preserve your oral health.
One of the initial signs of gum disease is inflammation, which can manifest as redness, swelling, or tenderness in the gums. You may also experience bleeding while brushing or flossing, which is often an early indicator of gingivitis, a milder form of gum disease. As the condition progresses, persistent bad breath, also known as halitosis, can become noticeable.
Loose teeth or a change in how your teeth fit together when you bite can signify a more advanced stage of gum disease. If left untreated, gum disease can lead to tooth loss and other serious complications.
Professional Diagnosis Methods
Dentists and dental hygienists play a vital role in diagnosing and treating gum disease. At your regular dental checkups, your dental hygienist will perform professional cleanings and thoroughly examine your mouth for any signs of gum disease. These examinations often involve specialized instruments and techniques to assess the health of your gums.
One common diagnosis method involves using a dental probe to measure the depth of the spaces between your teeth and gums, known as periodontal pockets. Healthy gums typically have shallow pockets, while deeper pockets can indicate gum disease. X-rays may also be taken to visualize the bone levels supporting your teeth, as bone loss is a common characteristic of periodontitis.
The information gathered from these assessments, combined with your medical and dental history, allows your dentist to determine if you have gum disease and accurately diagnose the severity of your condition.
How to Prevent and Treat Gum Disease
Prevention is key when it comes to gum disease. By adopting good oral hygiene habits, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing this common oral health problem. Brushing your teeth at least twice daily using fluoride toothpaste, flossing daily to remove plaque and food particles from between teeth, and rinsing with an antiseptic mouthwash are foundational practices.
If you're diagnosed with gum disease, multiple treatment avenues are available depending on the severity. Treatment aims to control the infection, reduce inflammation, and prevent further damage to your gums and teeth.
Effective Prevention Strategies
Taking proactive steps to safeguard your oral health is paramount, and practicing good oral hygiene diligently is the cornerstone of preventing gum disease. Brushing your teeth twice a day using fluoride toothpaste effectively removes plaque and debris from the surfaces of your teeth, inhibiting bacterial growth.
Flossing daily is just as crucial as brushing, as it removes food particles and plaque from between your teeth that your toothbrush can't reach. Supplementing brushing and flossing with an antimicrobial mouthwash further helps control bacteria in your mouth, promoting a healthier oral environment.
In addition to these practices, scheduling regular cleanings with your dental hygienist is vital. Professional cleanings provide a deeper level of cleaning, removing tartar buildup that you can't eliminate at home. These cleanings are essential for preventing gum disease and are a cornerstone of maintaining optimal oral health.
Current Treatment Options
Gum disease treatments vary widely depending on the stage and severity. In its early stages, non-surgical approaches are often effective in managing the condition. Scaling and root planing, a deep-cleaning procedure performed by a dental professional, removes plaque and tartar from below the gum line, smoothing the root surfaces to discourage further bacterial accumulation.
Antibiotics, either topical or oral, can help control bacterial infection and facilitate healing. For more advanced cases, periodontal surgery might be necessary. These surgical procedures aim to reduce pocket depth, remove infected tissue, and, in some cases, regenerate lost bone and gum tissue.
Gum surgery encompasses various procedures, including flap surgery, bone grafting, and guided tissue regeneration. The specific gum treatment recommended will depend on the individual needs of the patient.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the contagious nature of gum disease is crucial for maintaining oral health. While it's not directly transmitted person-to-person like a cold, certain behaviors can increase the risk of spreading bacteria. Recognizing symptoms, seeking professional diagnosis, and adopting effective prevention strategies are key to managing gum disease. Remember, good oral hygiene practices play a significant role in preventing its progression.
If you're concerned about your gum health or need professional care, consult with Club 32 Advanced Technology Dentistry. We offer expert dental services, from cleanings to more advanced gum treatments, ensuring your smile stays healthy and bright!
Frequently Asked Questions
Can you catch gum disease from sharing food or drinks?
Yes, sharing utensils or drinks can be a risk factor for gum disease. While not direct contagion, it increases the chance of exchanging saliva, potentially spreading the bacteria. Good oral hygiene and regular dental care minimize this risk.
Can you kiss someone with gum disease?
Kissing someone with periodontal disease can introduce bacteria into your mouth through the exchange of saliva. While not a guarantee you'll develop gum disease, maintaining excellent oral hygiene and a healthy immune system is crucial.
How long is gum disease contagious?
The duration of contagiousness varies depending on factors like the stage of gum disease and the presence of gum inflammation. It's best to practice caution until the infected individual has received appropriate treatment and their oral health has improved.
Need Assistance? We’re Here to Help
Our expert team is ready to support your dental health and well-being.
We are committed to offering personalized dental care solutions that promote a healthy smile.