New Paragraph
Essential Oral Cancer Screening Guidelines
Understanding Oral Cancer
Overview of Oral Cancer
Oral cancer refers to a type of cancer that develops in the tissues of the mouth, which includes the lips, gums, tongue, and the lining of the cheeks. The early detection of oral cancer is vital since it can significantly improve treatment outcomes. Oral cancer has a five-year survival rate of 57%, which means that just over half of individuals diagnosed are still alive five years post-diagnosis. Early detection increases the chances of successful treatment, making regular oral cancer screenings essential.
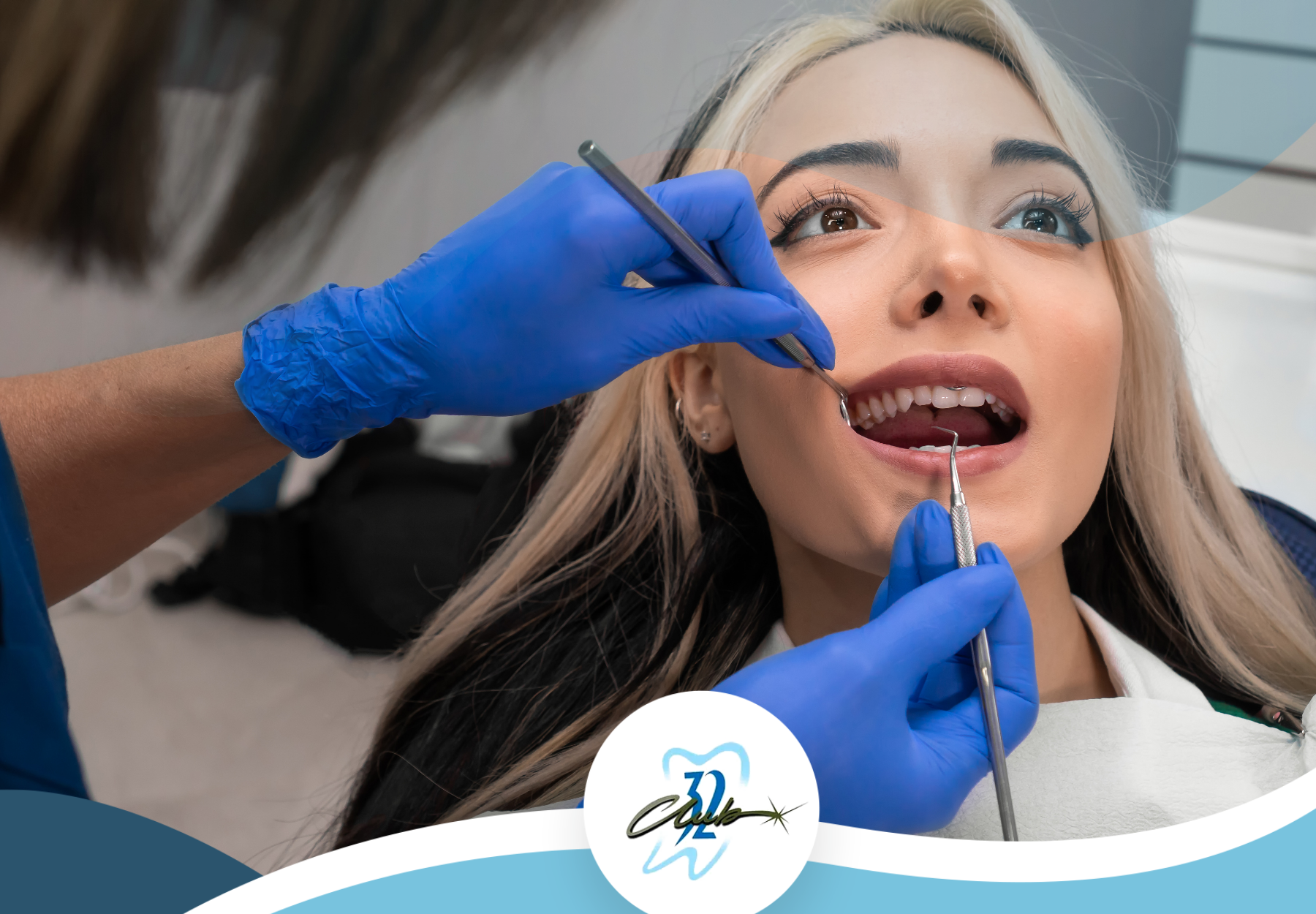
During an oral cancer screening, dental professionals examine the inside of the mouth for patches, sores, or abnormalities. Such screenings typically occur during routine dental visits and do not require special preparation. While oral exams can identify potential issues, a definitive diagnosis requires a biopsy to test abnormal cells for cancer.
Risk Factors for Oral Cancer
Several factors can increase the risk of developing oral cancer. These include:
| Risk Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Tobacco Use | This includes smoking cigarettes, cigars, pipes, and using smokeless tobacco products, which significantly raise the risk. |
| Alcohol Consumption | Heavy and frequent alcohol use can contribute to the development of oral cancer. |
| HPV Infection | Human papillomavirus (HPV), particularly strains associated with oropharyngeal cancer, increases the risk of oral cancer. |
| Sun Exposure | Prolonged sun exposure can lead to lip cancer. |
| Age | The risk of developing oral cancer increases with age, particularly for those over 45. |
| Gender | Males are more likely to develop oral cancer than females. |
Understanding these risk factors is crucial for individuals seeking to mitigate their chances of developing oral cancer. Lifestyle changes and regular screenings play a significant role in reducing risk. For more information on preventive measures, refer to our article on how to prevent oral cancer and learn more about specific types like preventing gum cancer and preventing tongue cancer.
Prevention and Risk Reduction
Preventing oral cancer and reducing the associated risks involve several strategies, emphasizing the importance of early detection, avoiding harmful behaviors, and protecting overall oral health.
Importance of Early Detection
Early detection is vital for improving outcomes in patients diagnosed with oral cancer. Oral cancer screenings are essential for identifying potential cancerous growths before symptoms appear, which enhances the chances of successful treatment. Dentists often include oral cancer screenings in routine exams, allowing for timely referrals for further diagnostic testing if suspicious findings arise.
The five-year survival rate for oral cancer stands at 57%, illustrating that early diagnosis can significantly impact a patient’s prognosis. Regular dental visits and immediate attention to concerning symptoms can facilitate early detection.
Behaviors That Increase Oral Cancer Risk
Certain behaviors can elevate the risk of developing oral cancer. Understanding these risk factors is crucial for prevention:
| Behavior | Increased Risk |
|---|---|
| Tobacco use (cigarettes, pipes, cigars, chewing tobacco) | Significant risk factor |
| Heavy alcohol consumption | Significantly raises risk, especially when combined with tobacco use |
| HPV infection (particularly type 16) | Linked to oral cancers |
Tobacco and alcohol consumption, particularly in tandem, significantly increase susceptibility to oral cancers. The National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research emphasizes these associations, urging individuals to avoid these high-risk behaviors.
Protecting Against Oral Cancer
Protective strategies can help individuals lower their risk of oral cancer. These include:
- Regular Dental Check-ups: Routine dental exams and cleanings enable early detection and treatment of any oral issues.
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Avoiding tobacco products, limiting alcohol consumption, and maintaining a balanced diet can significantly reduce risk.
- Vaccination: The HPV vaccine can help mitigate the risk of HPV-related oral cancers.
- Awareness of Symptoms: Being vigilant about any changes in the mouth, such as unexplained sores or lumps, can prompt early medical consultations. For additional information on recognizing early signs, see our article on early signs of oral cancer.
Employing these prevention strategies comprehensively contributes to reducing the risk of oral cancer and ensuring better health outcomes. For more specific prevention methods related to different types of oral cancer, visit our sections on preventing gum cancer and preventing tongue cancer.
Oral Cancer Screening Guidelines
Early detection of oral cancer is vital for treatment and improves the chances of successful outcomes. Understanding the roles of both dental professionals and individuals in screening can help in the prevention and management of this disease.
Dentist's Role in Offering Screenings
Dentists play a crucial role in the early detection of oral cancer. They typically incorporate oral cancer screenings into routine examinations. These screenings help identify potential signs of cancer before symptoms emerge, significantly enhancing the possibility of effective treatment.
The following techniques are commonly used during oral cancer screenings:
| Screening Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| Visual Examination | Inspecting the mouth for unusual signs or lesions. |
| Palpation | Feeling for lumps or abnormalities in the mouth and neck areas. |
| Oral Screening Dyes | Applying dyes to highlight any suspicious areas. |
| Special Lights | Using lights to detect irregularities in the tissue. |
| Photography | Documenting any abnormal areas for further assessment. |
These screenings can typically be completed in less than five minutes and do not provide a definitive diagnosis. If any suspicious findings are noted, dentists will often refer patients to oncologists for additional testing and diagnosis.
Self-Oral Cancer Screening at Home
While a dentist's assessment is crucial, individuals can also perform self-screenings at home to monitor for any changes. A self-oral cancer screening is not a replacement for professional check-ups, but it encourages awareness and proactive health management.
Individuals can follow these steps for a thorough self-screening:
- Find a Well-Lit Area: Good lighting is essential to see any abnormalities.
- Use a Mirror: Stand in front of a mirror and check both the inside and outside of the mouth.
- Check for Unusual Sores or Lesions: Look for white or red patches, lumps, or lesions that do not heal.
- Examine the Gums: Observe the gums for any swelling or changes in color.
- Palpation: Gently feel the neck and jaw for lumps or swollen areas.
While these self-examinations help in early detection, they underscore the importance of regular visits to a dentist for professional screenings. Maintaining good oral health habits can also contribute to risk reduction. For detailed strategies on reducing oral cancer risk, refer to our article on how to prevent oral cancer.
Being proactive about screenings and staying informed are essential steps in the fight against oral cancer.
Oral Cancer Screening Process
Understanding the process of oral cancer screening is crucial for early detection and prevention. The screening typically involves various techniques that help identify early signs of oral cancer, followed by potential follow-up tests to confirm any abnormalities.
Techniques Used in Oral Cancer Screening
The techniques employed for oral cancer screenings are generally quick and can be completed in less than five minutes during routine dental or physical checkups. These techniques aim to detect suspicious spots or lumps inside and around the mouth that may indicate the presence of cancer or precancerous conditions.
Common methods include:
- Visual Examination: The dentist will visually inspect the mouth, including the roof, inside of the cheeks, under the tongue, and other regions of the head and neck for any irregularities.
- Palpation: The dentist will feel the tissues of the mouth and neck for lumps or abnormalities.
- Oral Screening Dyes and Lights: Some professionals utilize special dyes or lights to enhance visibility of suspicious areas.
- Photo Documentation: Photos may be taken of abnormal areas to monitor changes over time.
- Brush Technique: A simple brush technique can be used to collect cell samples from suspected regions for laboratory analysis. This minimally invasive procedure aids in identifying cancerous or precancerous cells.
The aim of these techniques is to spot abnormalities such as patches, sores, and tissue irregularities inside the mouth.
Follow-up Tests After Screening
If any suspicious areas are noted during the initial screening, further follow-up tests may be necessary. These tests can include:
| Test Type | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Biopsy | Sampling tissue for laboratory examination to confirm the presence of cancer cells. |
| Imaging Tests | X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs may be ordered to assess the extent of the disease if cancer is suspected. |
| Lab Analysis | Examination of collected cell samples to identify any precancerous or cancerous changes. |
Follow-up tests are essential to ensure accurate diagnosis and to provide more information on the condition. Early detection is crucial, as identifying oral cancer at an early stage can lead to more effective treatment options.
For more information on the early signs of oral cancer, visit our article on early signs of oral cancer. Additionally, explore our guidelines on how to prevent oral cancer to learn more about protective measures.
Detecting Signs of Oral Cancer
Recognizing early signs and understanding risk factors can significantly impact the outcomes of oral cancer. In this section, we delve into the common symptoms of oral cancer and the high-risk behaviors that individuals should avoid to reduce their chances of developing this condition.
Common Symptoms of Oral Cancer
The most common signs of oral cancer include a flat, painless white or red spot, or a small sore in the oral cavity. While these abnormalities can often be harmless, it is crucial for individuals to inform their dentist about any of these symptoms for proper evaluation. Early detection enhances the effectiveness of treatment.
Routine preventive care, including regular dental check-ups and cleanings, plays a vital role in identifying and treating early signs of oral cancer. Individuals who notice any concerning symptoms should seek immediate dental attention.
High-Risk Behaviors to Avoid
Certain behaviors significantly increase the risk of developing oral cancers. Awareness of these factors is critical for prevention. Key high-risk behaviors include:
- Smoking: Tobacco use in any form is one of the leading contributors to oral cancer.
- Smokeless tobacco: This includes products like chewing tobacco, which can also significantly elevate cancer risk.
- Excessive alcohol consumption: Heavy drinking increases susceptibility to oral cancers, especially when combined with tobacco use.
- Oral HPV infections: Human Papilloma Virus, particularly type 16, is linked to cancers in the back of the throat. Preventative measures and awareness can help manage this risk.
By avoiding these high-risk behaviors and staying vigilant about changes in oral health, individuals can significantly decrease their risk of oral cancer.
Professional Intervention and Care
Involvement of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons
Oral and maxillofacial surgeons are vital members of the healthcare team that provides comprehensive care for oral cancer patients. They play a significant role in managing the condition by working alongside other healthcare professionals before, during, and after cancer treatment.
These specialists are trained to perform surgical procedures related to the mouth, jaw, and face, which are often crucial in addressing oral cancers. Their involvement is particularly important when surgical intervention is necessary, whether for tumor removal or reconstructive procedures following treatment. By being part of a multidisciplinary cancer care team, oral and maxillofacial surgeons contribute significantly to the overall management of oral cancer and related health issues.
Treatment and Care for Oral Cancer Patients
The treatment and care of oral cancer patients typically involve a combination of surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. Surgical methods may vary based on the stage and location of the cancer. In many cases, early diagnosis through vigilant oral cancer screening guidelines allows for less invasive treatments.
| Treatment Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Surgery | Involves removing cancerous tissues and may include reconstructive surgery to restore function and appearance. |
| Radiation Therapy | Utilizes high-energy rays to kill cancer cells and shrink tumors, often applied after surgery to eliminate remaining cancerous cells. |
| Chemotherapy | Employs drugs to target cancer cells, commonly used in combination with other treatments for better efficacy. |
Individualized treatment plans are developed based on the patient's specific circumstances, including general health, cancer stage, and preferences.
After treatment, ongoing care and monitoring are essential to manage side effects, ensure recovery, and detect any signs of recurrence early. Being aware of early signs of oral cancer and maintaining regular check-ups are crucial in the long-term management of oral health for cancer survivors.
Additionally, preventative measures, like reducing risk factors associated with oral cancer, should be emphasized. Understanding how to prevent oral cancer, including avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption, can play a significant role in reducing the risk of future occurrences.
Through a comprehensive approach that includes surgical expertise, treatment, and continuous care, oral and maxillofacial surgeons, along with the multidisciplinary team, provide essential support for individuals battling oral cancer.
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| White or red spots | Flat, painless lesions that can appear anywhere in the mouth. |
| Sores | Persistent sores that do not heal over time. |
| Difficulty chewing or swallowing | A sensation of tightness or pain when moving food in the mouth. |
| Changes in speech | Difficulty pronouncing words clearly or changes in voice quality. |
| Numbness | Loss of feeling in any part of the mouth or lips. |
Need Assistance? We’re Here to Help
Our expert team is ready to support your dental health and well-being.
We are committed to offering personalized dental care solutions that promote a healthy smile.